Time:2024-06-07 Views:1
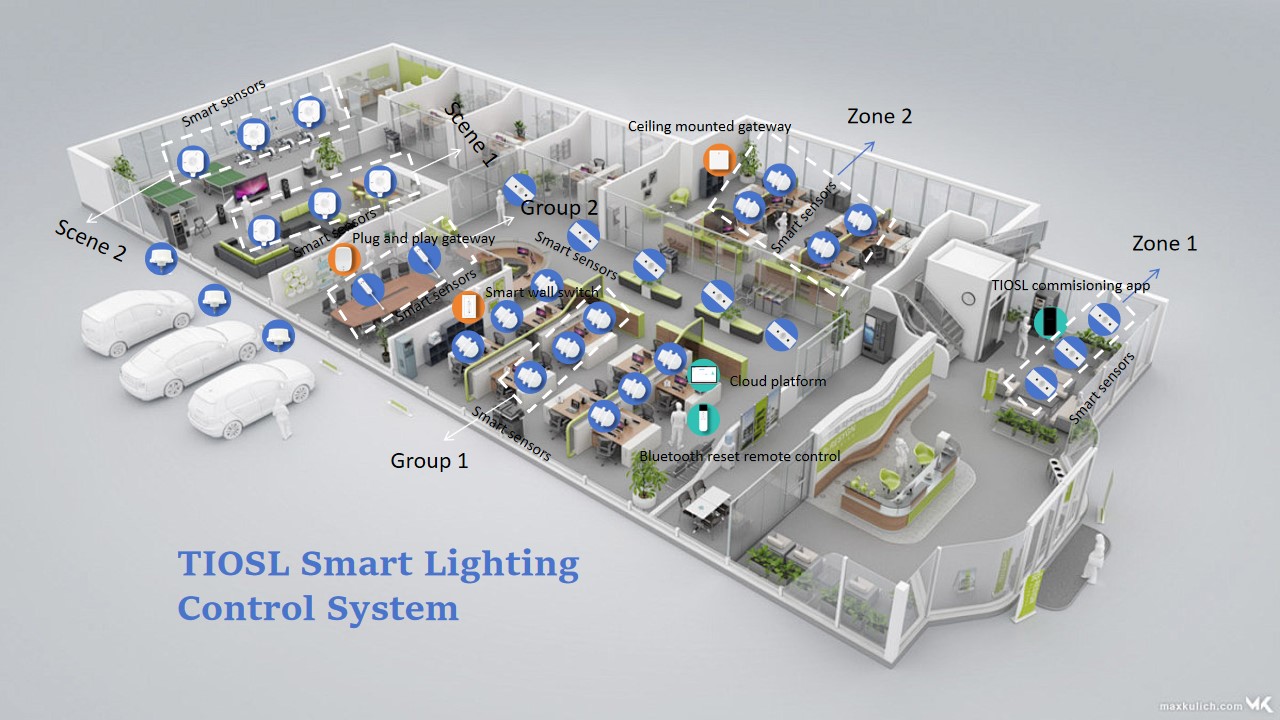
A multi-level management smart lighting control system integrates advanced technologies to manage and control lighting in various environments, enhancing efficiency, energy savings, and user comfort. Here’s an overview of its key components and functionalities:
1. System Architecture
Central Control Unit (CCU): The brain of the system, responsible for processing data, making decisions, and communicating with other system components.
Sensors: Including motion, occupancy, daylight, and temperature sensors, these devices provide real-time data to the CCU.
Controllers: Devices that receive commands from the CCU to adjust lighting levels, turn lights on or off, or change lighting colors.
Communication Network: Wired (e.g., Ethernet, power line communication) or wireless (e.g., Zigbee, Wi-Fi, Bluetooth) network that connects all components.
Automated Lighting Control: Adjusts lighting based on occupancy, daylight availability, and time schedules to optimize energy usage.
Zoning and Grouping: Allows for different lighting settings in various areas or zones, tailored to specific needs and preferences.
Scene Setting: Predefined lighting scenes can be programmed for different activities or times of day (e.g., meeting mode, relaxation mode).
User Interface: Mobile apps, touch panels, or web interfaces for users to manually control lighting and set preferences.
Energy Monitoring: Real-time energy consumption tracking and reporting to help identify opportunities for further savings.
Commercial Buildings: Offices, retail spaces, and industrial facilities can benefit from automated and flexible lighting control.
Public Spaces: Parks, streets, and transportation hubs can improve safety and reduce energy costs.
Educational Institutions: Schools and universities can create optimal learning environments.
